Redaction
What is Redaction?
Redaction is a data masking method that selectively removes or obscures specific information within a document or dataset, ensuring that sensitive details remain confidential. Though similar to other masking techniques, redaction differs in permanence and methodology. It goes beyond simply hiding or masking the information; it aims to render it unrecoverable or unreadable in its original form.
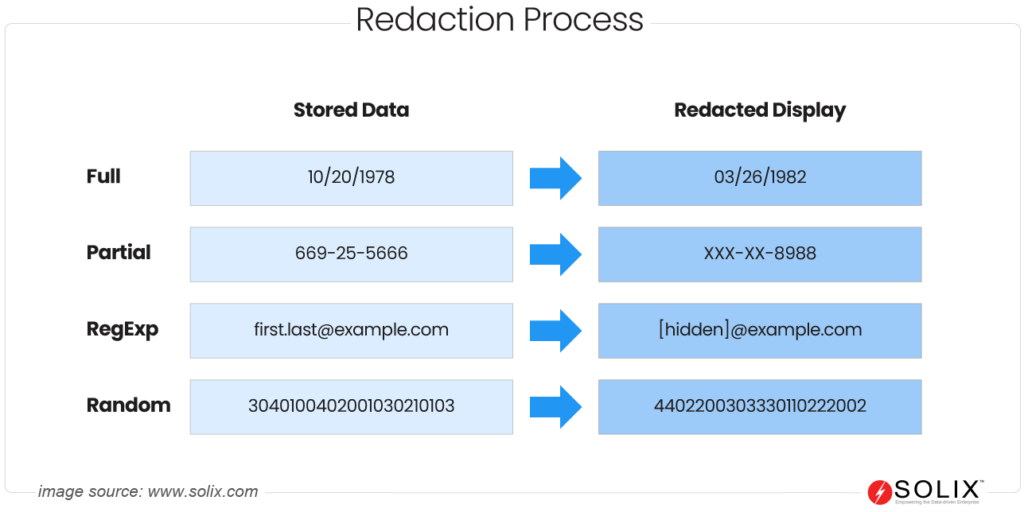
How does Redaction work?
Redaction Techniques
Redaction can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Black-box Redaction: Completely covering the sensitive data with a black box or other visual elements.
- Full Redaction: Obscuring all sensitive data, such as displaying it with empty spots or irrelevant values
- Partial Redaction: Obscuring only part of the sensitive data, such as displaying only the last four digits of a social security number.
Factors to Consider
- Technical feasibility: Choose a method compatible with your data format and processing capabilities
- Legal Requirements: Some regulations mandate specific redaction methods or retention periods. Make sure that your selected approach complies with relevant regulations.
- Data Utility: Certain methods, like blackouts or partial obfuscation, retain some data usability, while completely redacted data might become unusable for analytical purposes. Consider the intended use of the redacted data.
- Sensitivity of Data: Highly sensitive information like social security numbers requires blackboxing or complete deletion, while less sensitive data like addresses might be redacted with partial redaction or other masking methods.
Benefits of Redaction
- Mitigation of Data Breach Risks: Redacted data reduces the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized access and bolsters overall data security.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: It helps organizations maintain the privacy of sensitive information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR.
- Regulatory Compliance: It helps organizations align with industry-specific regulations and standards, safeguarding against legal repercussions related to data mishandling.
- Secure Information Sharing: Organizations can confidently share redacted documents internally or with external partners, facilitating collaboration while preserving data privacy.
Limitations
- Technical Limitations: Certain data formats or complex structures must be revised for effective redaction. Ensure your chosen method is compatible with your data format and technical infrastructure.
- Compliance Complexity: Different regulations might have varying data redaction methods and documentation requirements. Consulting legal professionals and thoroughly understanding relevant regulations are crucial to ensure compliance.
- Cost and Resource: Implementing and maintaining robust redaction solutions can require significant technical resources and financial investment. Evaluate the cost-benefit trade-off based on your specific needs and data sensitivity.
- Data Loss: Depending on the method, valuable data could be lost entirely. Overwriting or deletion permanently removes information, potentially hindering analysis. Consider substitution or blurring to preserve data utility, especially in research or analysis contexts.
Use Cases of Redaction
Here’s a closer look at its most common use cases:
- Analytics and Research: It balances discovery with privacy in analytical and research settings, preserving integrity and insights. It minimizes data leaks, upholds ethics, and empowers researchers for responsible and impactful discoveries within regulations.
- Non-Production Environments: To prevent unauthorized access, sensitive data must be redacted during development, testing, and training. It is also crucial for financial institutions and healthcare providers to ensure data security and privacy.
- Public Datasets: Redacting sensitive data before public dataset releases ensures legal compliance and ethical responsibility, fostering transparency. Government agencies and research institutions can adopt this practice to disseminate data responsibly for knowledge sharing.
- Data Privacy Regulations: It plays a crucial role in the enterprise security landscape by complying with data privacy regulations such as GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, LGPD, PIPL, etc. It removes sensitive information and aids organizations in avoiding hefty fines or penalties.
In conclusion, Redaction is a pivotal tool in data privacy, offering robust features for protecting sensitive information. With its ability to selectively conceal or obscure data, redacted data ensures compliance with privacy regulations while preserving usability. Its versatile applications across industries underscore its significance in safeguarding confidential data in an increasingly digitized world.
FAQ
How does Redaction differ from data masking?
While data masking involves altering sensitive data to preserve its format, redaction involves permanently removing or obscuring specific information, making it unreadable or inaccessible.
Can Redaction be undone once applied?
Unlike reversible data masking techniques, redaction is typically irreversible. The goal is permanently remove or obscure sensitive information from documents or datasets.
What are the legal implications for inappropriate redacted data?
Improperly redacted data can lead to legal consequences, including violations of privacy laws, breach of confidentiality agreements, and exposure to lawsuits for data breaches or unauthorized disclosures.





